m (→Roads in the South Central Region: Added carriage returns for SL work zone signs.) |
m (→True Elevation) |
||
| (14 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 268: | Line 268: | ||
=== True Elevation === | === True Elevation === | ||
The South Central Region practices the concept of True Elevation (TE) to better represent segments in relation to surroundings / ground level. In general, most segments should have an elevation of ''Ground'' unless they pass over another segment, waterway, or natural feature. '''Drivable and non-drivable segments are handled the same way with respect to elevation.''' | The South Central Region practices the concept of True Elevation (TE) to better represent segments in relation to surroundings / ground level. In general, most segments should have an elevation of ''Ground'' unless they pass over another segment, waterway, or natural feature. '''Drivable and non-drivable segments are handled the same way with respect to elevation.''' | ||
<font color="red">'''''NOTE: At this time, this is not a seek-and-destroy mission. Only fix true elevation as you encounter it.'''''</font> | |||
True Elevation can help the user identify an elevated segment by shading the edges of the segment. Currently, not all elevated segments are configured to display this. At this time, true elevation only affects the look of the map in the LiveMap. However, it is anticipated the Waze app will render elevated segments in the future. | |||
==== {{@|Definitions}} ==== | ==== {{@|Definitions}} ==== | ||
''Bridge'' | * '''Bridge:''' A ''bridge'' is defined as a segment which is elevated ''above ground level'' by means of a man-made structure, typically to pass over another segment, waterway/body of water, or a ground-level natural feature. This does ''not'' include segments which are elevated above surrounding ground level solely by earthen construction. | ||
* '''Tunnel:''' A ''tunnel'' is defined as a segment which passes below ground level (i.e., underground) by means of a man-made structure. This includes segments which pass under ground level segments via the use of a culvert or similar structure. This does ''not'' include segments which are below surrounding ground level but above ground (e.g., depressed freeways). | |||
''Tunnel'' | |||
==== {{@|Examples}} ==== | ==== {{@|Examples}} ==== | ||
* [https://www.waze.com/en-US/editor/?env=usa&lon=-95.73154&lat=36.16328&zoom=5 Simple Interchange] | * [https://www.waze.com/en-US/editor/?env=usa&lon=-95.73154&lat=36.16328&zoom=5 Simple Interchange] | ||
* [https://www.waze.com/en-US/editor/?env=usa&lon=- | * [https://www.waze.com/en-US/editor/?env=usa&lon=-97.78261&lat=30.53442&zoom=6 More Complex Interchange (requiring junctioning of ramp segments to maintain ground elevation)] | ||
* [https://www.waze.com/en-US/editor/?env=usa&lon=- | * [https://www.waze.com/en-US/editor/?env=usa&lon=-101.83730&lat=35.19289&zoom=5 Turbine Interchange - Amarillo, TX] | ||
* [https://www.waze.com/en-US/editor/?env=usa&lon=- | * [https://www.waze.com/en-US/editor/?env=usa&lon=-96.76415&lat=32.92438&zoom=4 Complex Interchange (High-Five in Dallas, TX)] | ||
* [https://www.waze.com/en-US/editor/?env=usa&lon=- | * [https://www.waze.com/en-US/editor/?env=usa&lon=-91.68015&lat=30.35592&zoom=4 Raised Freeway (over marsh land)] | ||
==== {{@|Visuals}} ==== | ==== {{@|Visuals}} ==== | ||
Below are two images showing the difference in Live Map rendering when True Elevation is not applied and when True Elevation is applied. Take note of the shading along the edge of the segment is missing when True Elevation is not used. | Below are two images showing the difference in Live Map rendering when True Elevation is not applied and when True Elevation is applied. Take note of the shading along the edge of the segment is missing when True Elevation is not used. | ||
'''* * * * * * NOTE * * * * * | '''* * * * * * NOTE * * * * * WAITING ON LIVEMAP UPDATE AND UPLOAD CAPABILITY ON WIKI TO RETURN. WILL REPLACE THESE WITH SCR EXAMPLE SOON. :) | ||
''' | ''' | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 301: | Line 300: | ||
==== {{@|Implementation}} ==== | ==== {{@|Implementation}} ==== | ||
* Elevation of overlapping segments should be set relative to each other, with the lowest segment as | * Any segment that intersects another segment at the same elevation must have a junction node. | ||
* Elevation of overlapping segments should be set relative to each other, with the lowest segment as ''Ground'' except when the lowest segment is a tunnel. | |||
* Only elevate / lower the actual bridge / tunnel section of the road. | * Only elevate / lower the actual bridge / tunnel section of the road. | ||
* Bridges should be cut at the start / end of the bridge where the land falls away. You can typically see guardrail at the start / end of the bridge section, an expansion gap in the pavement where the bridge starts / ends, and/or a pavement change (asphalt to concrete, for example). | * Bridges should be cut at the start / end of the bridge where the land falls away. You can typically see guardrail at the start / end of the bridge section, an expansion gap in the pavement where the bridge starts / ends, and/or a pavement change (asphalt to concrete, for example). | ||
** | ** Careful attention needs to be paid if a potential segment cut will occur within a very short distance of an existing node. | ||
*** If your new node would be placed within a few dozen feet of an existing node, you can either use the existing node as one end of the bridge, or, if desired, add the node for the elevation change and then add a junction box. | |||
*** If you are unsure which of the above methods is preferable in a given situation, please contact local leadership. | |||
** Maintain some uniformity for display purposes when determining where to make the cuts. | ** Maintain some uniformity for display purposes when determining where to make the cuts. | ||
* Only set elevation as low / high as necessary. For example, no segment should be elevation +2, unless it passes over another segment with elevation +1. | * Only set elevation as low / high as necessary. For example, no segment should be elevation +2, unless it passes over another segment with elevation +1. | ||
* Tunneled segments shall have lower elevation, relative to ground | * Tunneled segments shall have lower elevation, relative to ground. Consult the [[Tunnels|USA Tunnel Guidance]] on whether or not ''Tunnel'' should be checked. | ||
* Only segments which are actually '''underground''' should have negative elevation. | * Only segments which are actually '''underground''' should have negative elevation. | ||
* Tunnels should be cut at least 15m / 50ft before and after the tunnel, to allow time for the GPS to regain signal. | * Tunnels should be cut at least 15m / 50ft before and after the tunnel, to allow time for the GPS to regain signal. | ||
* '''The use of common sense is paramount in implementing True Elevation.''' | * '''The use of common sense is paramount in implementing True Elevation.''' | ||
Note: If you have any questions, please speak with leadership for your area. Also, if you use the ''Bridge tool'' to join segments, be aware this will raise the elevation of the joined segment and you must lower the joined segment as appropriate. | '''''Note:''''' If you have any questions, please speak with leadership for your area. Also, if you use the ''Bridge tool'' to join segments, be aware this will raise the elevation of the joined segment and you must lower the joined segment as appropriate. | ||
Latest revision as of 15:12, 21 June 2018
Roads in the South Central Region
Interstates in the region
Arkansas / Louisiana / Mississippi / Oklahoma / Texas
Road naming
Use the following designations when creating or editing numbered roads in the South Central Region.
| AR | LA | MS | OK | TX | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Interstates | I-XX | I-XX | I-XX | I-XX | I-XX |
| US Highway | US-XX | US-XX | US-XX | US-XX | US-XX |
| State Highway | AR-XX | LA-XX | MS-XXX | SH-XX | SH-XX |
| State Loop | AR-XX LOOP | SH-XX LOOP | Loop XX | ||
| State Spur | AR-XX SPUR | LA-XX SPUR | SH-XX SPUR | Spur XX | |
| State Park Road | Park Rd XX | ||||
| State Rec Road | Recreational Rd XX | ||||
| County Road | CR-XXX | Parish Rd XX | CR-XXX | Varies by Cnty | CR-XX |
| Farm/Ranch to Market | FM XX/RM XX | ||||
| Private Road | Private Rd XX |
Business Roads All business roads should be suffixed with BUS:
- Business Interstate = I-XX BUS
- Business US Highway = US-XX BUS
Other road names
The South Central Region conforms to the USA Standards for TTS abbreviations for prefixes and suffixes. Please see the Road Naming Abbreviations & Suffixes page for more details.
Non-drivable roads
Generally, if a road can't be driven on (e.g. Walking Trail, Pedestrian Boardwalk, Stairway, Ranch road in the middle of nowhere), then it should not be mapped in the South Central Region. We have chosen to implement this guideline because due to the way the routing engine works, Waze WILL route users to drive on these "Non-Drivable" road types.
Railroads mapped in the South Central Region should follow the current standard of editing. All crossings should be connected to drivable segments accordingly. If no crossing exists, elevate the segment accordingly.
ONLY enter a name for the railroad segment if the tracks are historical in nature, a major landmark, or a routine destination for Wazers. In the SCR, very few segments should be named and most 'routine destinations' will be covered by a Place point/area for the train station.
The Waze app now renders railroad tracks as such so naming serves little purpose any longer.
Special roads
- When not to divide a two-way road
- Divided Roads
- Carpool, HOV, Transit lanes
- Roundabouts and Traffic Circles
- Cul-de-sacs
- Dirt Roads. In the South Central Region ALL roads that are unpaved or gravel are considered dirt roads as this is how GPS Nav users (any brand) expect the "Avoid Dirt Roads" feature to behave. These roads should be deleted when going through farm land, ranch land, or mountainous areas throughout the state, as they are most likely base import roads and not real roads. For roads which are labeled with names and are actually dirt on SATIMG, please keep these and make them dirt roads. To do so, select the Local Street or Private Road type (as appropriate), then check the Unpaved box.
- Parking Lot Roads. Map parking lot roads (PLRs) that will allow proper navigation in to and out of a parking lot. A primary routing purpose for PLRs is to connect a parking lot that has entrances along two or more different named roads, to enable shorter / faster routing to a destination. The SCR standard for PLRs is to enable U-turns at the ends of each PLR segment. In the Waze app, U-turn-enabled PLR segments will support drivers that need to double-back on a segment. This will allow Waze to quickly route drivers who need to exit any parking lot the same way that they came in. This SCR guidance is true for gas stations, strip malls, shopping areas, and other PLAs where a PLR is appropriate. Remember that a parking lot area (PLA) does not substitute roads needed for actual navigation. While it is important to map appropriate PLRs, please follow guidance and do not add PLRs which are not necessary.
- Toll Roads. Only segments that actually contain a toll gantry should be marked as Toll.
- Frontage roads. Name as "Frontage Rd" unless the corresponding highway has an alternate name. I-635 Frontage roads are labeled as "Lyndon B Johnson Freeway" as that is the local name for I-635.
- Alleys and driveways are generally not mapped unless they are required for navigation. See Driveways for more information.
- Any road which is a main road for a state park can be a Primary Street . Other roads can be Local Street .
Turnarounds and Median U-Turn Segments (MUTIs)
Turnarounds Turnarounds (those labeled as Turnaround, not crossovers), should be classed as Local Street .
Median U turn segments (Louisiana) Dedicated median U-turn segments in the New Orleans metropolitan area (at least) should be unnamed.
A turn instruction override should be used such that a "U-turn" instruction is given when entering the U-turn segment.
For curved segments, the geometry of the segment should be set such that no instruction is given when leaving the U-turn onto the road. For straight segments, a turn instruction override may be used as well, set to "None".
Segment and turn restrictions
Information about setting partial restrictions on time or vehicle type on roads.
Information about soft and hard turns, turn restrictions, and time-based turn restrictions.
Functional Classification of Roads
The South Central Region participates in functional classification across all states. We promote a hybrid FC to ensure for the best routing possible for all Wazers. The hybrid FC basically means a state highway would never be typed less than Minor Highway (mH). See Road types and Road names to learn more about various road types and how functional classification applies.
Frontage roads
All frontage roads running along freeways and major highways should be set to Minor Highway .
In cases where a Wazer would go from Fwy > Ramp > Frontage Rd > Major , the Frontage Rd would be set as Minor with the Routing Type changed to One type higher or Preferred. This moves that section of road up in classification within the routing server but for appearance purposes, it keeps it as a Minor . Frontage road that dead ends should be set as Local Street . Small sections of Frontage Rd which just run parallel to a freeway and provide no entrance/exit to/from the freeway will match FC or be no higher than PS .
Only those rank 4 or higher can set the Preferred/One type higher routing flag. Once this flag is set, certain edits on the segment will be limited to those R4 and higher.
Turnarounds
Turnarounds (those labeled as Turnaround, not crossovers), should be classed as Local Street .
Functional Classification by State
Use the appropriate link below to access the correct Waze Functional Cross Reference chart and state DOT Functional Classification map for the state you are working in. Once you have reviewed the map, refer to the FC cross reference chart below to determine what road type and lock level should be assigned to the roads in the area. For roads that need to be locked at a higher level than you are able, change the street to the correct type, then request a lock from a higher-level editor.
| State | WAZE FC X- Reference | State DOT FC Map | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arkansas | AHTD FC Overlay for ArcGIS | The AR FC map is an overlay added to the base ArcGIS map. To use the overlay, click on the "Modify Map" in the upper right corner of ArcGIS. On the left side an "Add+" tab will pop up. Click on it and select "Add Layer from Web" and paste in the URL for the overlay provided by the link to the left. If you have never used ArcGIS before, you may be asked to create a Public Account. | |
| Louisiana | LaDOTD Interactive Online Map | Static FC maps are also available if desired. | |
| Mississippi | MDOT | Click on Functional Class Maps to find the various FC maps available. | |
| Oklahoma | ODOT ArcGIS Map | Static maps available here: ODOT Look in the middle of the page to find links for Rural Functional Class maps and Urban Functional Class maps. | |
| Texas | TX FC Chart | TxDOT Statewide Planning Map | Select Functional Classification & Urban Areas in the left menu to turn the FC overlap on. |
FC issues on State Maps
If you find any issues where FC changes unexpectedly such as in the image (the small section of green in between 2 red sections), please let the Regional Coordinator (RC) know exactly where this is located, so the appropriate DOT can be notified.

Road Lock Standards
In the South Central Region, we have a set minimum standard for locking roads based on segment type. Any road of a certain segment type must be locked at least to the rank (level) in the chart below. Roads may be locked higher for protection and special situations (areas with construction, tricky design, frequent mistakes, imaging inaccuracies, and the like), but should not be locked lower. If you find a road locked to a higher level than its minimum, please leave it locked no lower than that level when you have finished editing.
| Segment Type | Lock Level |
|---|---|
| Freeway | 5 |
| Ramp | 4 |
| Major Highway | 4 |
| Minor Highway | 3 |
| Primary Street | 2 |
| Local Street | Automatic (1) |
| |-|-|-|-|-|-|-|-|-| Railroad |-|-|-|-|-|-|-|-|-| | 2 |
| • • • • Ferry • • • • | 5 |
| Private Road | 2 |
Speed Limits
Please familiarize yourself with the information on the Speed Limits Wazeopedia Page.
Where speed limits change 
Speed limits should change where they legally go in effect for your state, that may be at the sign, a specified distance before the sign, or the nearest intersection. When a speed limit changes in the middle of a segment, a new junction should be added to support the SL change.
- However a new junction should never be added for a SL if it will be within 200 feet of an existing junction, or potential junction.
- A new junction should always be added if it will be more than 1,000 feet from the nearest existing or potential junction.
Creating a new junction for a speed limit change 
When creating a new junction solely for the sake of showing a speed limit change, you can attempt to get more value from the junction. Survey the area around the speed limit change, determine if there is a PLR or other segment which should be connected to the road and would result in a junction. You may find that there's a parking lot which could benefit from being added to the map within the allowable distance of 200 feet (or more depending on your area) to where the SL changes. In such a case connect that segment and use that junction. Otherwise you should create a new junction to show where the SL changes.
On roads where traffic for one turn direction typically backs up waiting to make the turn further than 200 feet, and traffic going straight or turning the other direction does not have to wait as long to pass through, turn delays can be affected even with the new junction 200 feet away. In these cases you may choose to extend the buffer zone to beyond the point where traffic backs up, and instead make the change at an existing junction node. These situations are governed by editor discretion and local guidance.


Work zones 
Speed limits in work zones are often lowered to protect workers and prevent collisions. If these speed limits appear on regulatory black and white signs, they MAY be added to the associated WME road segments. Speed limits should only be changed in work zones when the change will be in effect for at least 30 days.
Add the construction zone speed limit to the affected segments and place a [CONSTRUCTION] note on the map listing the official speed limit so when construction is complete, an editor can easily reset the speed limit.
True Elevation
The South Central Region practices the concept of True Elevation (TE) to better represent segments in relation to surroundings / ground level. In general, most segments should have an elevation of Ground unless they pass over another segment, waterway, or natural feature. Drivable and non-drivable segments are handled the same way with respect to elevation.
NOTE: At this time, this is not a seek-and-destroy mission. Only fix true elevation as you encounter it.
True Elevation can help the user identify an elevated segment by shading the edges of the segment. Currently, not all elevated segments are configured to display this. At this time, true elevation only affects the look of the map in the LiveMap. However, it is anticipated the Waze app will render elevated segments in the future.
Definitions 
- Bridge: A bridge is defined as a segment which is elevated above ground level by means of a man-made structure, typically to pass over another segment, waterway/body of water, or a ground-level natural feature. This does not include segments which are elevated above surrounding ground level solely by earthen construction.
- Tunnel: A tunnel is defined as a segment which passes below ground level (i.e., underground) by means of a man-made structure. This includes segments which pass under ground level segments via the use of a culvert or similar structure. This does not include segments which are below surrounding ground level but above ground (e.g., depressed freeways).
Examples 
- Simple Interchange
- More Complex Interchange (requiring junctioning of ramp segments to maintain ground elevation)
- Turbine Interchange - Amarillo, TX
- Complex Interchange (High-Five in Dallas, TX)
- Raised Freeway (over marsh land)
Visuals 
Below are two images showing the difference in Live Map rendering when True Elevation is not applied and when True Elevation is applied. Take note of the shading along the edge of the segment is missing when True Elevation is not used.
* * * * * * NOTE * * * * * WAITING ON LIVEMAP UPDATE AND UPLOAD CAPABILITY ON WIKI TO RETURN. WILL REPLACE THESE WITH SCR EXAMPLE SOON. :)
 |
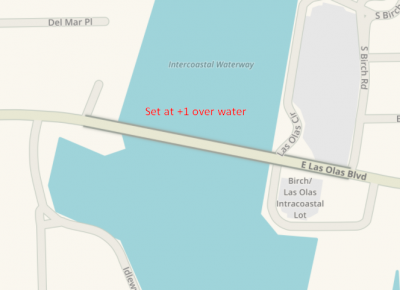 |
|---|---|
| Segment over water without True Elevation | Segment over water with True Elevation |
Implementation 
- Any segment that intersects another segment at the same elevation must have a junction node.
- Elevation of overlapping segments should be set relative to each other, with the lowest segment as Ground except when the lowest segment is a tunnel.
- Only elevate / lower the actual bridge / tunnel section of the road.
- Bridges should be cut at the start / end of the bridge where the land falls away. You can typically see guardrail at the start / end of the bridge section, an expansion gap in the pavement where the bridge starts / ends, and/or a pavement change (asphalt to concrete, for example).
- Careful attention needs to be paid if a potential segment cut will occur within a very short distance of an existing node.
- If your new node would be placed within a few dozen feet of an existing node, you can either use the existing node as one end of the bridge, or, if desired, add the node for the elevation change and then add a junction box.
- If you are unsure which of the above methods is preferable in a given situation, please contact local leadership.
- Maintain some uniformity for display purposes when determining where to make the cuts.
- Careful attention needs to be paid if a potential segment cut will occur within a very short distance of an existing node.
- Only set elevation as low / high as necessary. For example, no segment should be elevation +2, unless it passes over another segment with elevation +1.
- Tunneled segments shall have lower elevation, relative to ground. Consult the USA Tunnel Guidance on whether or not Tunnel should be checked.
- Only segments which are actually underground should have negative elevation.
- Tunnels should be cut at least 15m / 50ft before and after the tunnel, to allow time for the GPS to regain signal.
- The use of common sense is paramount in implementing True Elevation.
Note: If you have any questions, please speak with leadership for your area. Also, if you use the Bridge tool to join segments, be aware this will raise the elevation of the joined segment and you must lower the joined segment as appropriate.