| As of October 31, 2018[update], the road type Passageway should not be used in the USA. This road type is designed for other parts of the world, where some public roads accommodate only vehicles narrower than cars. At this time, DO NOT use the Passageway road type in the USA without explicit champ approval for each instance. |
Road types in the United States can be divided into three categories: public roads, other drivable roads, and non-drivable roads.
Public road types in Waze are determined by the FHWA functional classification of the road and, where applicable, by the highway system to which the road belongs.
| Some of the guidance for Road types may have specific localized adjustments for your local area. Be sure to familiarize yourself with these differences through the Mapping resources/States page. |
Overview 
Importance of road types 
Road types are important for both routing and map display:
- When planning a route, major roads will sometimes get priority over smaller roads.
- For longer routes, some lower road types will often be ignored outright in favor of higher-type roads.
- Since freeways are given the highest priority of all, having other high-type roads is necessary to provide viable alternatives to the routing server in case freeways are clogged with traffic.
- When viewing the map, more important roads should appear at the far zoom levels. Without proper types, the zoomed out display can be misleading.
- Certain other drivable road types generate transition penalties when a route leaves them onto a different road type.
- This can be useful for areas like private installations but can also cause dramatic and unexpected routing results.
Before editing 
Be sure that you are completely familiar with the articles on:
- The Waze Map Editor
- Creating and editing road segments
- Junction Style Guide
- Creating and Editing a roundabout
- At-grade connectors
Road types do not affect naming. See Road names for naming conventions.
Public roads 
Public roads are those that can be driven by anyone. Naturally, they are by far the most important roads on the Waze map.
The Freeway and Ramp road types each have their own special rules. The Major Highway , Minor Highway , and Primary Street types are designated using a set of minimum criteria, as explained below.
| Public roads are designated by a series of minimum criteria.
If a road meets any one criterion for a type, the road must be at least that type. For example,
|
A hybrid system 
Public road types in the United States are determined through a hybrid system of FHWA functional classification and U.S., state, and sometimes county highway systems. These systems work together to create a harmonious Waze map with excellent routing characteristics. Neither of these two facets of the road type system should be considered sufficient on its own, without the other. The road type guidance has been carefully crafted to join these two systems into one single contiguous Waze road type system.
Functional classification 
Functional classifications (FC) are determined using a set of criteria selected by the Federal Highway Administration (FHWA). These criteria include not only the physical attributes of the road but also efficiency of travel, number of access points, speed limits, route spacing, actual usage, and continuity. This can lead to quite different classifications for roads that appear similar. For example, a six-lane divided road in an urbanized area may be a Collector (Primary Street); a two-lane road through the middle of a town may be a principal arterial (Major Highway).
Functional classification is a national standard, but functional classification maps are published by state departments of transportation. Links to functional classification maps for each state can be found on the functional classification page.
Highway systems 
The Interstate Highway System (formally, the Dwight D. Eisenhower National System of Interstate and Defense Highways) is a nationwide network of freeways designated by Congress and administered by the FHWA and AASHTO, a nationwide organization of state departments of transportation with governmental support. The system facilitates high-speed travel throughout the nation.
The United States Numbered Highways, or U.S. Highways, system is a nationwide integrated network of roads also designated by Congress and administered by the FHWA and AASHTO. While many of the routes in this system have been superseded by the Interstate Highway System, they remain important as direct links between regions not served by the new system, and as alternatives to Interstate travel in the case of heavy traffic or incident.
Each of the fifty states (along with the District of Columbia and some of the United States's overseas territories) has a numbered state highway system. These systems are designated and administered by their respective state legislatures and departments of transportation as statewide networks of important travel links between cities and communities of those states. The roads in these systems, while of lesser national importance, are nevertheless essential for travel within the state.
In addition to their state highway systems, some states designate county routes which are important for travel within a county. These routes serve important functions in a short-distance capacity.
Highways 
A highway is an arterial road.
Highway roads are the backbone of the traffic network. They serve a dual purpose:
- to carry traffic over long distances, from one city to another, and
- to carry traffic from collector roads to freeways, where applicable.
Several systems of numbered highways exist in the United States:
- the Interstate Highway System
- the United States Numbered Highways
- various State Highway systems
- various County (or Parish) Highway systems, in some states
Waze's definition of "highways" includes Interstate, US and state highways, but it also includes all other roads that are classified as arterial roads under the FHWA functional classification lists maintained by state governments, even though they may not be part of any numbered highway system.
Functional classification of roads is determined more by how the roads are used than by how they are constructed, and the criteria are slightly different between urban and rural areas. Because of this, some urban roads may be classified as arterials and have highway types in Waze, even though they appear very similar to other non-highway roads. In using functional classification and numbered highway systems, the decision on which roads should be classified as highways rests ultimately with the governments that build and maintain the roads.
Waze distinguishes three classes of highway: Freeway , Major Highway , and Minor Highway .
Freeway 

A freeway is a highway designed for high speed traffic, with fully controlled access over entrance to, and exit from, the highway.
Freeway is the highest functional class of road.
The following roads shall be classified as Freeway :
- All Interstate Highways.
- This includes all roads classified in FHWA's functional classification as Interstates.
- This includes three-digit Interstate spurs and loops (e.g., I-610; I-585).
- This includes the few grade-intersected, undivided, and/or narrow portions of the Interstate Highway System.
- This does not include Interstate Business Loops and Business Spurs (e.g., I-69 Business Loop), unless they meet the standards for Other Freeways and Expressways defined below.
- Roads classified in FHWA's functional classification as Other Freeways and Expressways which meet the criteria of a controlled-access highway:
- No at-grade crossings.
- No at-grade intersections.
- No direct property access.
- No stop lights (except sometimes on ramps).
- No stop signs.
- Except at the beginning or end of the controlled-access roadway, connected to other roads exclusively by interchanges:
- Entrance via ramps only, typically with acceleration zones.
- Exit via ramps only, typically with deceleration zones.
- Note: Many freeways continue as non-controlled-access roadways; the road should be set as Freeway until the point at which access becomes non-controlled.
- Note: Some states refer to this class as Other Freeways. In these states, every road in this class is a Freeway.
For information on how to best layout freeways and their junctions, please review the section on freeways in the Junction Style Guide. For specific guidelines in other countries refer to this page for more information.
Major Highway 

Principal arterials are the primary routes for traveling throughout the country, from one city to another, over long distances. Many principal arterials are freeways or expressways, but many others are not.
As a nationwide system, the United States Numbered Highways, or U.S. Highways, system provides a direct links between regions not served by the Interstate Highway System, and as alternatives to Interstate travel in the case of heavy traffic or incident.
The following roads are to be classified, at minimum, as Major Highway :
- Roads classified in FHWA's functional classification as Principal Arterials or Other Principal Arterials.
- Roads classified in FHWA's functional classifications as Other Freeways and Expressways which do not meet the criteria for Freeway.
- This includes partially-limited-access roadways (or "expressways"). These are roads that have a lot of the characteristics of freeways, but also have occasional at-grade intersections with other roads.
- Note: Every partially-limited-access roadway is a Major Highway; this does not mean that every Major Highway must be partially-limited-access.
- Note: "Expressway" is used as a shorthand term for partially-limited-access roads. This does not mean every road named "Expressway" is a Major Highway.
- Note: Some states refer to this class as Other Freeways. In these states, every road in this class is a Freeway.
- Roads in the United States Numbered Highways system (US Highways).
- This includes Alternate (ALT), Bypass (BYP), Connector (CONN), Truck, and Scenic US Highways.
- This does not include Business, Spur, and Loop US Highways.
- Business routes (Spurs and Loops) in the Interstate Highway System (e.g., I-69 Business Loop).
Minor Highway 
Minor arterials (or other arterials) are secondary routes for traveling between cities over moderately long distances. Minor or other arterials are classified in Waze as Minor Highways.
Each of the fifty states (along with the District of Columbia and some of the United States's overseas territories) has a numbered state highway system. Roads in these systems are designated and selected by their respective State Departments of Transportation as part of statewide networks of important travel links between cities and communities of those states. These roads, while of lesser national importance, are nevertheless essential for travel within the state.
The following roads are to be classified, at minimum, as Minor Highway :
- Roads classified in FHWA's functional classification as Minor Arterials or Other Arterials.
- Signed, numbered routes in state, D.C., and territorial highway systems.
- This includes Alternate (ALT), Bypass (BYP), Connector (CONN), Truck, and Scenic state highways.
- This includes Spur state highways when they are used to connect state highways with other state highways, US Highways, or Interstates; i.e., Spur highways which are used like Connector (CONN) highways.
- This does not include Business (BUS), Loop, and other Spur state highways.
- Business (BUS), Loop, and Spur US Highways.
Note: Not every state highway system is the same. Some state systems may be overinclusive, whether because of differing standards or because of political corruption and pork barrel spending; as such, your state may make exceptions where some lesser state highways are better represented by the Primary Street type. Contact your regional coordinator before making these decisions.
Ramps 


The following are to be classified as Ramp .
- Roads which connect roadways to other roadways as part of an interchange. This includes all freeway exits and entrances.
- Roads connecting freeways and highways with Rest areas, parking areas, and service plazas (e.g., "to Service Area").
- Jughandles.
- Median U-turn Intersection (MUTI) and "Michigan left" segments.
- J-turn (RCUT/"Superstreet") segments.
- Displaced Left Turn (DLT) left turn segments.
The following are not to be classified as Ramp .
- At-grade connectors, unless they fit into one of the exceptions (see article).
- Turn lanes.
Ramp names do not appear on the client application map, but do appear in the text for routing directions. Entrance and exit ramps often contain a lot of text which is duplicative of roads already in the area, so this text is suppressed until the user actually needs it. This is also the reason for using the ramp type for named MUTI and jughandle segments—the text is needed for effective navigation instructions but would needlessly clutter the ramp.
Information on how to lay out ramps and set the proper angles from the main road can be found in the Junction Style Guide.
Streets 
The Street types are for local and short-distance travel. Street types are used at the beginning and end of long routes as well.
Primary Street 
Collectors are roads used with medium-low traffic densities which are used to bring traffic from local streets to arterials and vice versa. Collectors are classified in Waze as Primary Streets.
Some states designate county routes which are important for travel within a county. These routes serve important functions in a short-distance capacity.
The following roads are to be classified, at minimum, as Primary Street :
- Roads classified in FHWA's functional classification as Major Collectors or Minor Collectors and paved with a hard surface.
- Signed, numbered county routes (and, in Louisiana, parish routes) paved with a hard surface.
- Business (BUS) and Loop state highways, and Spur state highways which are not used as connectors, paved with a hard surface.
- Frontage roads which serve as the means of access between freeways/expressways and surface streets, if not otherwise classified.
- Some functional classification maps are not produced in high enough detail to determine the class of frontage roads. On maps that are produced in high detail, frontage roads are almost universally classified as Major Collectors or higher.
Unpaved roads – including gravel, macadam, and dirt roads – are considered on a regional basis. Check your state page or contact your regional coordinator.
Note: Some states or counties may designate county routes differently than others. Check your state's page for possible exceptions to this rule.
As stated above, frontage roads should generally be set to at least Primary Street , if not marked as a higher type on a functional class map.
Many frontage roads are used as "feeder roads" or "access roads", often the primary or only means of entering and exiting a freeway. Setting these to the "street" type, as has been done in the past, has the potential to invalidate good routes which use freeways and major/minor highways. To ensure that routing works, always use at least "primary street" for frontage roads that are used in this way. It may be desirable to set the entire frontage road to the same type to achieve a more contiguous map appearance.
Street 

Any road for public travel which does not meet the criteria for any other type shall be classified as a Street . Shown as "local roads" in some functional classification maps; not shown at all in others.
Passageway 

As of October 31, 2018[update], the road type Passageway should not be used in the USA. This road type is designed for other parts of the world, where some public roads accommodate only vehicles narrower than cars. At this time, DO NOT use the Passageway road type in the USA without explicit champ approval for each instance.
Service Road 
| The Service Road type is no longer available. Use other road types for service roads. |
- For guidance on mapping service roads AKA frontage roads, see the service road page and the section above.
Quick reference chart 
Refer to this chart to determine the road type of a given paved public road based on the functional class.
To use this chart, first determine the functional class of a road, and whether it is a signed, numbered highway in a particular highway system.
Where the column for the road's highway system and the row for the road's functional class meet, you will find the proper road type for that particular road.
A number of examples are given below the chart.
| Highway Systems | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Interstate | Interstate Business Loop/Spur | US Hwy (incl. some special routes) | US Hwy BUS, SPUR, LOOP | State Hwy (incl. some special routes) | State Hwy BUS, SPUR[a], LOOP | County Route | Locally-maintained | ||
| example | I-10 E | I-94 Business | US-190 | US-460 Business | SR-23 | SR-400 Loop | CR-15 | Robertson St | |
| F u n c t i o n a l C l a s s |
Interstate[b] | Fw | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Other Freeway[c] | n/a | Fw | Fw | Fw | Fw | Fw | Fw | Fw | |
| Other Expressway[d] | n/a | Major | Major | Major | Major | Major | Major | Major | |
| Other Principal Arterial[e] | n/a | Major | Major | Major | Major | Major | Major | Major | |
| Minor Arterial[f] | n/a | Major | Major | Minor | Minor | Minor | Minor | Minor | |
| Major Collector | n/a | Major | Major | Minor | Minor | PS | PS | PS | |
| Minor Collector | n/a | Major | Major | Minor | Minor | PS | PS | PS | |
| Local/not mapped | n/a | Major | Major | Minor | Minor | PS | PS | Street | |
^a When a state highway "SPUR" route is used to connect a state highway with another state highway, a US highway, or an Interstate (i.e., when it is used as a connector/CONN route), use the first state highway column.
^b Also known as Principal Arterial - Interstate.
^c Also known as Principal Arterial - Freeway.
^d Also known as Principal Arterial - Expressway.
^e Also known as Principal Arterial.
^f Also known as Other Arterial.
For example,
- An Interstate Business Loop classified as a Minor Arterial is a Major Highway .
- A US Highway classified as a Minor Arterial is a Major Highway .
- A US Highway Spur route classified as a Minor Arterial is a Minor Highway .
- A State Highway classified as an Other Freeway is a Freeway .
- A State Highway classified as a Collector is a Minor Highway .
- A County Route classified as a Minor Arterial is a Minor Highway .
- A County Route classified as a Collector is a Primary Street
- A locally-maintained road classified as an Other Principal Arterial is a Major Highway .
- A locally-maintained road classified as a Collector is a Primary Street .
| Fw | Freeway |
| Major | Major Highway |
| Minor | Minor Highway |
| PS | Primary Street |
| Street | Street |
Exceptions
If a road has a higher or lower type than what's specified in these rules, there may be a reason for it. Special rules are used to determine the road types of roundabouts and at-grade connectors.
Routing road type
Apart from changing the nominal road type, level 4 editors can also change the routing road type (also known as routing preference) to one type higher or lower, which only affects long-distance aspects of road type behavior while maintaining the same appearance, best continuation and detour prevention behavior of the nominal road type. These exceptions to the rules should be reviewed with local leadership before implementation.
Continuity
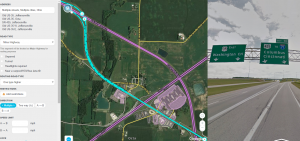

One common reason for a road to be set to a higher type is for the purpose of maintaining continuity between two roads with higher types. Promotion for continuity is usually indicated by signage: A certain less important road is signed as the way to get between two different more important roads.
For example, a freeway exit from I-70 is signed as "Exit 142: US-40 / Gratiot", indicating that this is the intended way to get to US-40, with Principal Arterial functional class. Between the ramps and US-40 is CR-30 with Local functional class. The rules on this page would normally dictate that this road be set to Primary Street, but in long-distance routing it may be removed from consideration, or pruned. This can be prevented either by assigning the Major Highway type outright or by assigning the Minor Highway type with a +1 routing road type, which would cause it to be treated like a Major Highway for long-distance routing. Use of routing road type is preferable to avoid unintended side effects on the behavior and display of the road.
Certain situations may require continuity upgrades even without signage to support them. Examples include but are not limited to:
- Sparsely populated areas connected by long roads with lower functional class
- Places where highway designations end abruptly, such as jurisdictional boundaries
- Alternate routes used as detours for main highways subject to frequent or long-term closures
- Urban or suburban areas in the midst of redevelopment, where functional class may be out of date
- Connecting roads that may be too short to be noticed during state functional class assignment
When promoting for continuity, the effective road type of the connecting road should match the lower of the two roads that it connects, similar to type selection for at-grade connectors, up to Major Highway. Since Major Highway is never pruned, there is no need to promote something to Freeway with routing road type for continuity reasons alone, and the nominal Freeway road type should only be used for controlled-access highways that meet the criteria above.
Continuity upgrades prevent Waze from pruning out valid routes, and in extreme cases they can mean the difference between getting a good route and getting no route at all.
Unpaved checkbox 
The ![]() checkbox is an attribute that can be applied to any road type. It indicates that a road is not paved with asphalt or concrete. The unpaved attribute affects routing over drivable road types; it does not really affect non-drivable road types, since the client does not use them for routing. Based on user preference, destination, and other settings options, the Waze client may avoid routing them over otherwise drivable segments when the 'unpaved' attribute is checked.
checkbox is an attribute that can be applied to any road type. It indicates that a road is not paved with asphalt or concrete. The unpaved attribute affects routing over drivable road types; it does not really affect non-drivable road types, since the client does not use them for routing. Based on user preference, destination, and other settings options, the Waze client may avoid routing them over otherwise drivable segments when the 'unpaved' attribute is checked.

When to select the Unpaved attribute
Any drivable road which is not paved with asphalt or concrete should have the Unpaved attribute box checked.
Check your state's page for details on whether there are additional guidelines for roads that are in uncommonly poor condition by local standards or contact your Regional Coordinator for further guidance.
User setting options for the Unpaved attribute
This attribute has the unique property in that Waze users may select when not to be routed over unpaved road segments. Users may choose:
- 'Dirt roads - Don't allow' - Avoids through-routing on all unpaved roads
- 'Dirt roads - Avoid long ones' - Avoids through-routing on long unpaved roads
- 'Dirt roads - Allow' - Allows through-routing that could include unpaved road(s) (i.e. ignores whether roads have the unpaved attribute checked)
Other drivable roads 
Off-road / Not maintained Road 
| Use extreme caution when mapping through roads with this type! In an emergency, such as wildfire or flooding, Waze responders may mark primary through roads in an area as closed on behalf of public safety. However, if off-road segments appear to provide alternate through routes, and responders miss closing them, Waze may offer those segments instead regardless of penalty. Waze may also route using off-road segments if they appear to bypass private or fee-collection gates. As of October 2018[update] do not map through roads using this type unless you make certain that the roads (1) are passable, if only barely, by ordinary passenger vehicles or (2) would not be routed as alternate routes in emergencies or into restricted areas. |

The Off-road / Not maintained (formerly Dirt Road / 4x4 and Unpaved) segment type had the unique property that Waze users could ask not to be routed over it. That function has now shifted to the Unpaved attribute check box (see above).
Off-road / Not maintained roads are typically deeply rutted with thick mud, irregularly shaped rocks, fallen trees, branches, and deep streams, creeks, or river crossings. A typical car would bottom out, get stuck, or even break an axle trying to traverse these types of road segments. The vast majority of vehicles would not be traveling down these roads. This segment type should strictly be used by a type of hard terrain/special vehicle.
Any road for which high-clearance vehicles are recommended or required should be assigned the Off-road / Not maintained type, if it is mapped at all, regardless of its maintenance status.
Currently, Waze does not plan to support a 4X4 vehicle type in the client app, but the developers have left this option for editors to map these paths, so they can be displayed on the map. They have an extremely high penalty associated with them and will not be suggested for any through routes in most ordinary circumstances.
Check your state page for details on whether your state follows unique guidelines for hard terrain/special vehicle roads, or contact your Regional Coordinator for further guidance.
Parking Lot Road 

Parking lots, along with other publicly accessible roads such as alleys that should not be used for traffic routing unless directly at the start or end point of a route.
- See this additional page for more details on how to map parking lots.
| This section was updated as of January 14, 2015[update] to clarify when to use PLR vs Private Roads . |
- Use Parking Lot Road type for all necessary segments in the Parking Lot.
- Parking Lot Road type should be used inside Apartment Complexes, Schools, and Universities unless it meets the criteria for Private Road found in the next section below.
- Parking Lot Roads have a transition penalty when exiting the Parking Lot road segment. This should prevent Waze from routing you through a Parking Lot or an alley as a shortcut.
- Parking Lot Roads can be used to avoid "missing road" automated Map Problem reports.
- Parking Lot Roads can be used to prevent Waze from assuming drivers driving slowly or parked in the parking lot are in a traffic jam on the main road -- draw in the drivable portions of the parking lot that are near outside roadways.
- Waze will not highlight slow speeds (automatically detected traffic jams) on Parking Lot Roads
Additional information on this topic can be reviewed in the forums.
Information on mapping a parking lot landmark "place" is covered here.
Private Road 

Private roads are useful for the following situations:
- Gated communities with controlled access
- Schools and Universities (gates / guard)
- Businesses with controlled access (gates / guard)
- Campgrounds or trailer parks (designed for short term guests)
However, using private roads in some of these situations may require more complex mapping as covered in the article Private Installations. Be sure to read through that article before setting a whole neighborhood to all private roads.
As with Parking Lot Roads , a route over a Private Road will incur a transition penalty upon leaving it for another road type. This transition penalty keeps Waze from routing Wazers through a private area as a shortcut. Unlike Parking Lot Roads , however, Private Roads do not suppress automated traffic-jam detection.
- Never use the Private Road type for unrestricted public roads
- Do not use the Private Road type to try to force waze to route around slow (damaged or under construction) public roads. Talk to a routing expert to find out if there are any good solutions.
- Private Road may be used for a public street that has a legally enforceable sign for local traffic only.
- Waze handles Private Roads similarly to how it handles Parking Lot Roads , but not exactly the same.
- Similarity: Waze routing adds a penalty to a route that goes from a Private Road segment to a segment of a different type.
- Difference: Waze will highlight traffic slowdowns on Private Roads .
Emergency Vehicle and DOT Service Roads 

Limited-access service roads, such as those marked for "emergency and authorized vehicles only" should not generally be mapped, and if there is a need to map them, they should not support routing nor appear like other roads. The clearest way to do this is to map them using the Private Road type, add partial restrictions on them to prohibit routing for all times and vehicle types and include a description within the restriction to explain the reason for mapping. Another, older method also involves using the Private Road type, disconnecting the limited-access road and locking as high as possible. This is also valid. Examples of such roads include fire roads prohibited to all non-service motor vehicles, patrol roads for park service vehicles, and service cutoffs across the medians of divided highways.
Ferry 
• • • • • • • •
| Prior to 2016[update] the Ferry Road type was not to be used. Since that time, there have been changes to the Routing server that allow the use of the Ferry Road type. |
The ferry road type should only be used where a road crosses a body of water through the use of an automotive ferry. For more on how to map ferries see Ferries. The ferry road type is useful because it causes the Waze client to display a "ferry" symbol for routes that include a ferry segment.
The ferry road type is treated by the routing server as a minor highway. The speed for the ferry road type is fixed at a very slow speed typical of watercraft, and not estimated from user speeds.
| If the ferry you are working on crosses an area well covered with GPS traces, OR travels at higher than normal speeds, please notify your Regional Coordinator. Additionally, if you have issues with routes passing thru a ferry segment, please contact your Regional Coordinator. |
Non-drivable roads 
Walking Trails 
For further information on the mapping of | | | | | Walking Trail | | | | | (known as routable pedestrian path in US English), | | | | | Pedestrian Boardwalk | | | | | (known as non-routable pedestrian path in US English or | | | | | Stairway | | | | | road types, see pedestrian path.
Railroad 
|-|-|-|-|-|-|-|-|-| |-|-|-|-|-|-|-|-|-|
| The guidelines below have been updated to reflect new standards on naming of railroads as of June 28th, 2016. |
| The guidelines below have been updated to reflect new standards on junctioning of railroad grade crossings as of September 19, 2018. |

The railroad road type serves two purposes in Waze. First, it provides drivers with visual orientation relative to railroad and light-rail tracks. More importantly, in the common case where passenger-carrying tracks lie parallel with roads, mapping the tracks allows Waze to recognize and discard spurious speed data from people Wazing on the train. This prevents corruption of speed data for the adjacent road.
Use the following guidelines when mapping railroad segments:
- Do NOT enter a name for the railroad segment unless the tracks are historical in nature, a major landmark, or a routine destination for Wazers and your local state/regional wiki guidelines allow for such naming. The Waze app now renders railroad tracks as such so naming serves little purpose any longer. (See more below on Naming railroad segments.)
- Always select "None" for the city name. This avoids city smudging.
- Lock the segment at L2.
- Do not map railroads below ground, as they do not serve either of the two purposes outlined above. This is especially true in urban areas where underground rail lines are common, and their appearance on the map would be confusing to drivers.
- Set the elevation just as you would a drivable segment. When tracks junction a road on the ground, the Elevation should be set to Ground.
- In specific circumstances, create junctions between drivable roads and railroads at grade crossings.[rr] Otherwise, do not junction grade crossings. The resulting elevation conflicts are acceptable.
- Set railroad to 2-way directionality
- When mapping railroad tracks, focus on those near drivable roads.
- Map rail yards simply, with one railroad segment along either edge of the yard's tracks.
- Map industrial spurs only if they cross drivable roads.
- Do not map every piece of parallel track, such as in sidings or yards, or industrial spurs that do not cross any roads. Your work may otherwise be seen as clutter.
- Multiple parallel lines at crossings:
- At most crossings, there should be only one railroad segment mapped and no more than two parallel railroads mapped at any crossing.
- Parallel lines are to be at least 6m apart
- In general, there is no reason to have multiple lines mapped. When not at a crossing, even four parallel lines can be easily mapped as a single railroad segment in Waze.
- Keep segment lengths under 10,000 meters – the longer the segment length, the more sluggish the editor is to respond to changes.
- Do not map railroads using a drivable road type (streets, primary streets, etc.); it could be a hazard to human life if drivers were routed to them.
^rr Adding a junction node for a grade crossing only benefits routing if both (1) between the existing junction nodes on the drivable road on either side of the grade crossing, there is at least one destination on one side of the crossing and room for cars to back up waiting on the other; and (2) the tracks support regular, scheduled train traffic. If either of these elements is missing, adding a junction node for the grade crossing will not benefit routing and may in some cases degrade routing. If it is difficult to determine whether regular, scheduled trains use the tracks, you may assume they do if the tracks appear active and well maintained.
Use the following guidelines when naming railroad segments, only if allowed by your local wiki guidelines:
- For urban rapid transit and light rail systems you may optionally use the name of the transit authority and the name of the line, separated by a hyphen (e.g., "MBTA - Green Line", "RTA - Riverfront Streetcar").
- If a system has only one line, of course, use its name alone (e.g., "Detroit People Mover").
- If multiple lines share the same track or run on parallel tracks, include all lines (e.g., "Metro Rail - Red/Purple Lines").
- However, if a rapid transit system is so complex that including all line names would lead to an absurd result on some railroad segments, use the name of the system alone (e.g., "BART", "MTA") throughout the system.
- Federal DOT Railroad GIS: http://fragis.fra.dot.gov/Apps/GISFRASafety/
Runway/Taxiway 

⁃ ⁃ ⁃ ⁃ ⁃ ⁃ ⁃ ⁃ ⁃ ⁃
Airport runways and private airstrips may be mapped using the Runway/Taxiway road type. The Runway/Taxiway type is for display only and must never connect to drivable road segments. If a drivable road and a runway cross, set the elevation of the road below that of the runway and ensure there is no connection. Draw each runway as a single segment and lock it to prevent lower-ranking editors from attaching a road. Do not form junctions where runways cross each other.
Name each runway using the word Runway and the runway designations with the lower number first and a hyphen between runway numbers (e.g., "Runway 16-34"). For parallel runways of the same designation, append the appropriate suffix to each of the runways (e.g., 16L-34R & 16R & 34L). For the "City" field of runway segments, check "None" to avoid any chance of city smudging.
Despite its title, the Runway/Taxiway road type should never be used for an aircraft taxiway because it would render the same as a runway and confuse the display. Taxiways not intended for frequent access by street vehicles should not be mapped at all with any road type. Taxiways that do commonly serve street vehicles as well as aircraft, for example at fly-in communities, may be mapped as Streets provided they remain disconnected from any runway.
Special case roads not covered 
There are a number of other types of roadways and lane types which are not directly covered with the current options above. In some cases there are plans to add some of these special cases, but in the mean time the following guidelines are the best that can be done with the current settings.
Bus or taxi only lanes 
When a road or lane is designated for bus or taxi use only, mark that road segment(s) with an allowed time based segment restriction for bus and/or taxi. The entire segment, right lane, center lane, or middle lane can be selected as appropriate on the second pop up window of the time based segment restriction. This will prevent the Waze router from using that segment(s) for general traffic, since the majority of the users will not be able to use that lane. It will only route if the taxi or bus type of vehicle is set in the user's settings. (Taxi is currently available but bus is a potential future selection). Set the turn restrictions as appropriate for the legal usage by taxi and/or bus vehicles.
Change the road segment(s) to the proper road type based on the functional classification and the Waze correlation table. A Private Road segment is no longer required.
If a road is one-way, but allows bus or taxi traffic to flow the other direction, leave the road as one-way with the normal flow of traffic, add the time based segment restriction for the Bus and/or Taxi in the appropriate direction. There is no need to create a second road traveling the opposite direction for the bus and taxi-only traffic.
Driveways 
Many residents of urban communities have very short driveways between the named road that they live on and the garage or carport on their property. In general these very short segments should not be mapped, because they have no name, would clutter the map in the client app, take a lot of time to draw, and would greatly increase the overall size of the Waze mapping database with very little return.
In the case of very long driveways, it may be helpful to a driver to see the driveway mapped on the client app or even necessary for Waze to determine how to reach the destination. In those cases it may be prudent to add a road. See the article on Driveways for more information.
