k (→Routing requests: wikilink avoid toll roads) |
kGeen bewerkingssamenvatting |
||
| Regel 73: | Regel 73: | ||
For this reason it is important to keep long segment lengths before junctions if traffic congestion at the junction might affect exits differently. | For this reason it is important to keep long segment lengths before junctions if traffic congestion at the junction might affect exits differently. | ||
To understand this problem better, consider if we add a short Seg8 between Seg7 and Jnct4. Let's say the traffic exiting Seg10 backs up all the way to Seg7 (easy enough, since Seg7 is short). Because Seg7 only has a single exiting segment (Seg8), the routing server is only able to collect a single average speed &mdash it can no longer distinguish traffic by where it is going ''after'' Seg8. Now the through traffic going to Seg9 appears to Waze to slow down through Seg7, even though it doesn't in reality. At a minimum this will cause an incorrect ETA for routing, and it might actually cause traffic to be rerouted unnecessarily, and less optimally, through another route. Hence if there is a chance that traffic that goes in different directions at a junction experiences different congestion, keep the segment before that junction long. | To understand this problem better, consider if we add a short Seg8 between Seg7 and Jnct4. Let's say the traffic exiting Seg10 backs up all the way to Seg7 (easy enough, since Seg7 is short). Because Seg7 only has a single exiting segment (Seg8), the routing server is only able to collect a single average speed — it can no longer distinguish traffic by where it is going ''after'' Seg8. Now the through traffic going to Seg9 appears to Waze to slow down through Seg7, even though it doesn't in reality. At a minimum this will cause an incorrect ETA for routing, and it might actually cause traffic to be rerouted unnecessarily, and less optimally, through another route. Hence if there is a chance that traffic that goes in different directions at a junction experiences different congestion, keep the segment before that junction long. | ||
Note this data is not presented to users through the Waze Map Editor, but is only visible to the routing server. | Note this data is not presented to users through the Waze Map Editor, but is only visible to the routing server. | ||
Versie van 2 aug 2013 01:39
Client based routing
Calculating an optimal route is a difficult task. While the client device app has a routing algorithm included, this is not used unless there is no connection to the Waze server.
Speculation
The routing algorithm used by the Waze server is not publicly disclosed and the following is based on observation, speculation, and some information revealed by Waze staff. We can assume that the operation of the routing server is considered to be proprietary and a competitive advantage to Waze. We can also assume that it is subject to change, and that any information that has been revealed may be incomplete or out of date.
What has been confirmed is the Waze Map Editor (WME) displays the overall average speed for a segment for each direction of travel through the segment. Also the routing engine uses real-time speeds (from recent Waze app users in front of you when available) and combines the historical speed of the segment broken down into 10-15 minute chunks. Also the time to pass through a segment is tracked separately for each route out of a segment. For example if a segment ends with a left and right turn (no straight let's say), then the routing engine isolates the time through the segment to turn left and the time through the segment to turn right. This detailed speed information is proprietary & is part of the data Waze sells/plans to sell and won't be displayed through the editor.
Routing requests
When you request a route calculation, the request is sent to the Waze server. That route is then transmitted back to your client device and displayed.
The requests for routing vary according to the settings you have chosen on your client device. Under Navigation you can choose:
- Fastest or shortest route
- Whether to allow or avoid toll roads
- Whether to allow dirt roads, never allow dirt roads, or to avoid long dirt roads
- Whether to avoid major highways
The shortest route refers to physical distance. Most people will usually prefer the Fastest route option; 100km of freeway is better than 90km of country roads.
Missing roads and incorrect junction connections
Waze tries to find the best route between you and your destination based on your navigation settings. Obviously it can only route based on roads that it knows about, so your route will not be optimal if a better route does not have all the roads with correct connections in the Live Map.
Real-time current road speeds
We can be confident that Waze uses real-time reports of current road speeds by preference over historical average road speeds. We know that Waze uses traffic congestion reports to reroute around slow traffic. Early versions of the client would also report when traffic speeds were good - this was removed due to map clutter. But Waze will still be receiving this information. We can assume that the speed of any wazer ahead of you on a stretch of road will be the speed used when your route is calculated.
As the number and density of Wazers grows this real-time data takes on a greater importance. This emphasis is partly a reflection of Waze's original goal to create optimal commutes. As Waze has grown to be used as a more general purpose GPS navigation device over roads less travelled, the historical average road speeds becomes more important.
Since Waze uses the time you expect to be at a road segment to calculate the expected speed on that segment, it cannot use real time data when you trip time moves into a future time slot. So trips of more than 30 minutes (and on average more than 15 minutes) will include future time slots where current traffic data is not available when initially calculated. When you enter a new time slot, real-time traffic data may be available which may cause your client to recalculate your ETA and reroute you at that point.
Fastest routing
Waze knows the average speed of every confirmed road between you and your destination. The Waze server can calculate which list of roads to take to minimize the total travel time.
While every request is processed in real-time, by observation it appears that Waze caches some requested routes or major points. This means if it already knows the best route from B to C, and you ask for a route from A to C, it may just calculate the best route from A to B, once it checks that there isn't a better route bypassing B altogether. This does mean that when there is a Live map update some routes may be less than optimal for up to a day as routes are cached and recalculated.
While a complex calculation, calculating the optimal route is possible. The complexity arises over the "average speed" of the roads.
Changes in route due to different origin
Consider calculating a route from A to Z. The suggested route may be A to B to C to D to Z. Then calculate the route from B to Z. You may get a suggested route of B to C to E to Z. At first glance, this suggests one route is not optimal.
We can guess at what might be happening. There may be a problem associated with the possible caching of routes. Or there may be a "timing window" effect. The different arrival time at C may change the best route to Z. Or there may be a fine tuning effect in the route, perhaps to avoid too many turns. So by dropping the segment A to B, the segments C to E to Z no longer exceed some threshold.
This effect can be observed while driving. If you recalculate a route to a destination while driving along an already calculated route to that same destination, the route may change.
This are old reports where wazers have not offered a route to bypass heavy traffic, but do receive a new route when manually asking for it. It may be they would have been offered that alternative route at that point anyway, whether or not there was bad traffic ahead. It does raise the question as to when and how Waze considers rerouting, but these may have been addressed in the current version. Certainly Waze does offer new routes sometimes.
Changes in routes due to different route lengths
In addition, it is known that the Waze routing engine can't calculate every possible route for long distance routes, so takes shortcuts for longer routes, potentially resulting in the route changing dramatically when lengthened slightly. According to Waze support (as of July 2011), the section of a route more than 10 km from each endpoint is heavily weighted towards non-streets (i.e. "Primary Streets" or the various Highway types). My personal guess is that it simply ignores streets outside of the 10 km radius from the endpoints when doing its calculations to speed up the calculation. The specific quote from support was: "Above some distance (currently 10KM) from both end points (start and destination) the server prefers to go through non streets. Now as it happens here - this small distance was the difference between being less than or over 10KM. Now the penalty of going through a street in this case is high - so the server prefers the highway." In this particular case, the observed behavior was that extending the route by a short distance caused Waze to suggest a very different (and much longer, both in distance and estimated time) route.
Problems with average road speeds
If the average road speed is not correct, then the route will not be optimal. However, it is never recommended to delete segments in order to reset the average road speed for that segment. Waze uses the data from Wazers traveling through the segments to update the average speed. If you suspect Waze is not using certain segments along a route, there are a number of other reasons that can cause such a situation. Don't assume deleting the segment is the place to start.
The following are reasons why the routing engine may not use the average road speed.
Time of day variations
Consider a road that most Wazers drive at 5pm when the average speed is 12 mph. You choose your route at 10am when the road is clear and the average speed is 60mph. It is the best road to take, but Waze chooses a different route because it has no information about the speed at 10am and assumes the speeds is 12mph all day.
You can, of course, drive the road yourself, and Waze will eventually learn the speed for that time. We do not know how long Waze holds the older data in computing the average speed. However if Waze does discard old time information, you may not accumulate new time faster than it is discarded. It is also possible that your times are being ignored as being abnormal.
More Waze users would help fix this.
Turn delays
On a segment of a road, your average speed can be very different depending on what you do at the end of the segment. Traffic going straight through a traffic light might go very fast while traffic turning left might wait a very long time. A freeway exit lane might go fast while traffic continuing hits congestion.
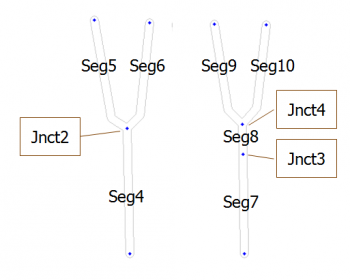
Waze has the ability to separately track the average speed of traffic that passes through a segment, but exits to different segments. The routing engine takes this into account. In the diagram, multiple times are tracked for traffic flowing through Seg4 based on the segments to which it exits. There are then two average drive times for:
- Seg4 to Jnct2 to Seg5
- Seg4 to Jnct2 to Seg6
Traffic building up on Seg4 that turns right to Seg6 will not affect the route timing for the traffic also using Seg4, but instead turning left to Seg5. For this reason it is important to keep long segment lengths before junctions if traffic congestion at the junction might affect exits differently.
To understand this problem better, consider if we add a short Seg8 between Seg7 and Jnct4. Let's say the traffic exiting Seg10 backs up all the way to Seg7 (easy enough, since Seg7 is short). Because Seg7 only has a single exiting segment (Seg8), the routing server is only able to collect a single average speed — it can no longer distinguish traffic by where it is going after Seg8. Now the through traffic going to Seg9 appears to Waze to slow down through Seg7, even though it doesn't in reality. At a minimum this will cause an incorrect ETA for routing, and it might actually cause traffic to be rerouted unnecessarily, and less optimally, through another route. Hence if there is a chance that traffic that goes in different directions at a junction experiences different congestion, keep the segment before that junction long.
Note this data is not presented to users through the Waze Map Editor, but is only visible to the routing server.
Waze Map Editor changes
The average speed of a road can be dramatically altered by editing in Waze Map Editor (WME). Consider a 50m length of road driven in 36 seconds. An editor extends this length of road the full 10km length. WME now records this road as 10km long, but also driven in 36 seconds for an average road speed of 1000km/hour. Therefore be cautious of significantly changing the length of roads. Instead consider drawing new roads and linking them.
Traffic lights and stop signs
Waze does not record the location of traffic lights. While some GPS navigation offers guidance like "turn right at the next traffic light" the information is frequently incomplete, incorrect or outdated. The consensus view is that Waze should not record the location of traffic lights.
Waze does take traffic lights and stop signs into account by noting the effect they have on traffic speed. Consider a traffic light with long waiting times. The road segment leading to that traffic light will have a low average speed. If the average speed (based on the average waiting time) becomes low enough, a longer route that avoids the light will become the preferred route. This has been observed in practice and is an example of emergent behaviour. Waze isn't programmed to avoid traffic lights but it will avoid slow roads; if the traffic lights make the road slow then Waze will avoid them.
Some drivers will regularly take longer routes—even winding through side streets—to avoid any stops or traffic lights. Waze has been known to suggest this, and also known to revert back to waiting at lights when better average speed information is collected from the side streets. But note that this can be less than optimal due to the turn delays discussed above.
Outdated and abnormal road speeds
Road conditions change, construction work comes and goes, and average road speeds can change dramatically. One day you may be stuck behind a truck, and another day you may be crawling along the roads at 2 a.m. transporting your pet goldfish. Or your GPS might have a glitch and show you travelling at 1,000 mph.
In short, average speeds can change over time, and recorded times can be abnormal or just plain wrong—and can stay wrong for a very long time.
We can assume Waze is aware of this. There is some evidence that abnormal road speeds and old road speeds are discarded, or at least not used in calculating the average speeds of roads.
Average road speed "shrinking window"
If there are enough recorded speeds on a road, then Waze uses a shrinking window of speeds to better estimate the average speed at the time you are travelling on it. Waze uses the speed of each road segment (in both directions) in intervals as small as 30 minutes. So a two-way road may have up to 48 average road speeds. We can assume that when there are insufficient records for an individual time slot, a wider time range is taken—up to a full day. As the road is driven more, the time slot would shrink down to 30 minutes.
We can speculate that there may be additional information used that is based upon the day of the week. There is some observational evidence that a road that is busy on weekdays and not used for routing will be chosen as the optimal route on weekends.
At some point, Waze would also need to consider the months of the year as seasonal variations can affect the speed of the roads.
Waze uses the average road segment speed for the time slot that applies at the time you are expected to arrive at that road segment.
Because of this "time window", Waze will suggest different routes at different times of day. This is dependent on how many times are recorded on the roads along the route. If they're all recorded at about the same time of day, then the time window will not help. If 1,000 times are recorded at about 5 p.m. and 2 times are recorded at 10 a.m., then your 10 a.m. average speed will still mostly be based on times from around 5 p.m.
Routing algorithm refinements
Routing options
It's easy to see how routing options can be implemented. For example, to minimise turns we can add a time penalty for fastest routing or a distance penalty for shortest routing, when calculating the fastest or shortest route.
Junction penalties
Currently Waze applies a five-second time penalty when calculating a route that passes through a junction. While not an unreasonable approach to dealing with intersections, it has generated some flawed routing and is being reviewed.
One major issue arises in long highways which may be made up of hundreds of segments connected together, as this may add a penalty of as much as five minutes to a trip, even though the intersections are not real. This supports the arguments of those who aim to have a clean edit of maps where junctions are only used when necessary. In practice, we need to deal with the map as it stands. An automated tool to remove the junctions is needed as the manual work that is required is enormous.
The routing problem can be fixed in a variety of ways. One could:
- Not apply the penalty when there are no other existing roads meeting at the junction;
- Not apply the penalty when you cross a junction onto a road with the same name;
- Not apply the penalty when the road you are travelling on is a higher class (e.g. highway versus street, primary street versus street), where we can assume the higher class road has the right of way; or
- Not apply the penalty at all when travelling on freeways, motorways and highways.
Even if a road is correctly connected with no unnecessary segments, the junction penalty can still give incorrect results. For example a busy highway may be correctly connected to the ramps along its length. A quiet country road running in parallel may not have all the minor connecting roads recorded; it looks like a straight section of road with no junctions. Waze may choose the country road as the preferred route because of the lack of junctions.
What to do if you think the generated route is wrong
Firstly, use the option to generate alternative routes. This may give you some clues as to why Waze is offering that route.
Secondly, if you think there is a better route, check in WME that the roads are all connected along the route.
Thirdly, post a message detailing the problem route - origin, destination and a WME permalink to the Navigation forum. Other eyes will check it, and you may indeed find a flaw in the Waze routing algorithm. Fixing it may make it better for everyone.
Change of Routing
When Waze receives notification of traffic conditions it uses the actual speed of roads on your route, rather than the average speed. This is based only on the automatic traffic condition reports - light, moderate, heavy traffic or complete standstill. Manual reports of traffic jams and accidents are for your information only and do not change routing.
It may be that even with the traffic reports, there is no better route and Waze will not offer you one.
You are the driver
Waze can never see that the traffic light is green going straight, or know that today is a public holiday. It can offer you guidance as to what is the best route under average conditions. But you are the driver and you are in the best position to make the decision for today under today's conditions.
If everyone followed Waze directions and never drove on a new route, Waze may never learn that route is better. When Waze is recording your travels, every trip helps make Waze better for everyone. That includes when you think you know better. Sometimes you will be right. And sometimes you will be wrong. But it is better to find out you are wrong so you can choose the better route. And when you are right, all Waze users benefits by sharing in your knowledge.