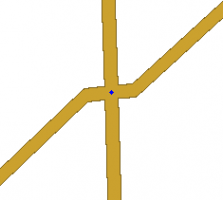
Similar to diverging roads that intersect at odd angles, crossing roads can do the same thing. When these intersections are mapped as seen here with these odd angles, complications can occur.
Geometry nodes bring the actual junction close to 90 degrees. Zoom in to the intersection and add a single geometry node on each side as close to the junction point as possible. This will give the more desirable 90 degree angle, and it will still be virtually invisible to client app users making it look like the physical world. This image is what is seen when zoomed in as close as possible. Zoomed back out, it looks just like the map image showing the junction without any geometry nodes.
Here is a real world example at a close zoom level where you can still see the geometry adjustment. With that adjustment in place, the junction will produce predictable turn left and right navigation instructions while the roads still appear to meet at the real-world angle in the client app.
Plantilla:ReturnJSG