(→Exceptions: writing style corrections) |
m (→Exceptions) |
||
| Línea 57: | Línea 57: | ||
=== Exceptions === | === Exceptions === | ||
A junction with more than one segment leaving it at an angle less than {{ | A junction with more than one segment leaving it at an angle less than {{:How_Waze_determines_turn_/_keep_/_exit_maneuvers/Stay threshold}} can give an instruction to '''all''' the segments, or '''none''' of the segments. Some of these scenarios are listed below: | ||
* If none of the segments leading out at less than {{:How_Waze_determines_turn_/_keep_/_exit_maneuvers/Stay threshold}} are a better match for name or segment type, tehy will all get instructions. This applies even if one of those has a departure angle of 0° from s-in. (This is also touched upon in the [[Junction_Style_Guide/Interchanges#Wayfinders|wayfinder section]].) | * If none of the segments leading out at less than {{:How_Waze_determines_turn_/_keep_/_exit_maneuvers/Stay threshold}} are a better match for name or segment type, tehy will all get instructions. This applies even if one of those has a departure angle of 0° from s-in. (This is also touched upon in the [[Junction_Style_Guide/Interchanges#Wayfinders|wayfinder section]].) | ||
*There will '''not always''' be a ''best combination''. | *There will '''not always''' be a ''best combination''. | ||
Revisión del 05:06 23 jun 2014
| This revision of the page is currently undergoing modifications. The information and guidance is currently considered accurate enough to be followed now. Content is being prepared by one or more users. Do not make any changes before you post a message in this forum. |
A somewhat simplified description of this is covered in the Junction Style Guide. Additional routing information is covered in the article Routing server.
The original text provided by Waze staff which inspired this page was proven slightly inaccurate, and was difficult to comprehend it was replaced on 06/22/2014.
A simplified easy to understand interactive version of this page is available here.
Definitions
To better be able to put the algorithm into words, we have to name each of the road segments that connect to a junction. These are subjective names, they are relative to which segment the junction is being approached from, and which segment the routing server wants to navigate to after passing through the junction.
Start with the junction in the middle.
- s-in: The segment the vehicle is on as it approaches the junction will be called s-in.
- s-out: The segment the vehicle is being routed onto after it passes through the junction will be called s-out. This can be any of the other segments connected to the junction, which will also be one of the segments named below as s1, s2, ... etc..
- s1, s2, s3, s4, etc.: All the segments connected to the same junction, (including s-out) will each be named consecutively as s1, s2, etc., for as many segments as there are… sN. One of these numbered segments will also be s-out.
- Best Continuation: One of the segments leaving the junction will be considered the 'Best Continuation'. This is the segment that Waze determines is what drivers would consider the "no turning path" or "going straight" through the intersection. This segment will get a 'continue' instruction, which is ignored by the client app. The criteria Waze uses to determine which segment is the 'Best Continuation' is explained below.
- Primary road: refers to a highway segment ( Freeway , Major Highway , or Minor Highway ), not a Primary Street .
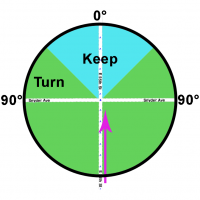
- The angle is the angle from the origin to the destination. A perfectly straight road with a junction in the middle would have a turn angle is 0°. The angle then gets wider as you turn to either side. A perfect left or right turn would be 90°. A U-turn at a junction between two segments would represent a 180° turn.
(A turn less than How Waze determines turn / keep / exit maneuvers/Stay threshold will give a keep/stay instruction, vs. a turn more than How Waze determines turn / keep / exit maneuvers/Turn threshold which gives a turn instruction.)- In technical terms: The angle between the linear segment between the last geometry node of s-in and the junction and the linear segment between the junction and the first geometry node of sN is the supplementary angle to the angle of sN.
| Angles | ||
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
| Standard Angles | 37° Angle | 90° Dogleg Geometry Node |
- A Normal Roundabout is one which has
- Four (4) or less exits,
- All exits leave the roundabout (from the perspective of s-in) at a normal angle.
- A Normal Angle is 0° or 90° to either side, ±15°. (See roundabout angle for more information)
- An Abnormal Roundabout is one which has
- Five (5) or more exits,
- At least one exit leaves the roundabout (from the perspective of s-in) at an abnormal angle.
- A Abnormal Angle is anything other than; 0° or 90° to either side, ±15°. (See roundabout angle for more information)

Best Continuation
In order to determine if s-out is the 'real' continuation of s-in, Waze does the following:
- If the angle between s-in and s-out is less than How Waze determines turn / keep / exit maneuvers/Stay threshold, it is selected as the real continuation, unless one of the following are present.
- There is another segment (s1, s2, ...sN) with an angle less than How Waze determines turn / keep / exit maneuvers/Stay threshold which has a better matching segment name & segment type to s-in than s-out does. (e.g. it has the same segment name and type as s-in and s-out doesn't; it has the same segment name as s-in and s-out doesn't; it has the same segment type as s-in, and s-out doesn't.) Segment name is more important than segment type.
- There is another segment(s1, s2, ...sN) with an angle less than How Waze determines turn / keep / exit maneuvers/Stay threshold which has the same segment name & segment type as s-out.
If a 'best continuation' is determined, Waze will not give an instruction going onto that segment.
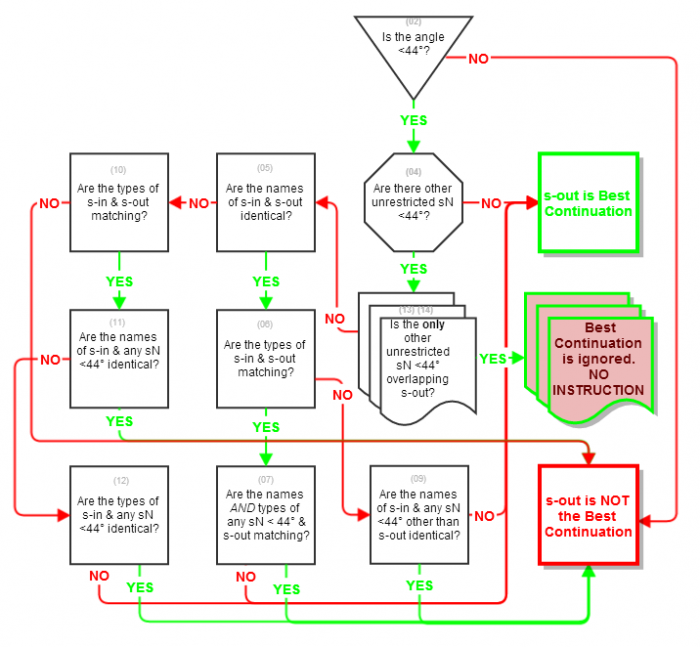
Exceptions
A junction with more than one segment leaving it at an angle less than How Waze determines turn / keep / exit maneuvers/Stay threshold can give an instruction to all the segments, or none of the segments. Some of these scenarios are listed below:
- If none of the segments leading out at less than How Waze determines turn / keep / exit maneuvers/Stay threshold are a better match for name or segment type, tehy will all get instructions. This applies even if one of those has a departure angle of 0° from s-in. (This is also touched upon in the wayfinder section.)
- There will not always be a best combination.
- When s-out has the same segment name and segment type as s-in, but another s-N also has the same segment name and type as s-N, neither will be considered the best continuation.
- A segment (s1, s2, ...sN) leaving the junction at less than a How Waze determines turn / keep / exit maneuvers/Stay threshold angle, which has the turn into it from s-in restricted in WME will not be considered in this algorithm as a 'best continuation', or as a sN, even if it has a departure angle of 0° from s-in.
The algorithm
The description below fits a right turn in a Right-hand traffic country (e.g. the USA). Left turns are symmetrical to right turns.
The algorithm iterates over a list of conditions. As soon as a condition is met, the relevant instruction is determined, and the algorithm terminates.
The list of conditions
- If the junction has only 2 segments, the instruction is: 'CONTINUE'.
By design the client does not give this instruction. - If s-out is determined to be the best continuation of s-in (see explanation on 'best continuation' above), the instruction is: 'CONTINUE', which implies that the driver is not turning (i.e., going straight through the junction).
By design the client does not give this instruction. - If the angle between s-out and a straight line is larger than 45 degrees, the instruction is: 'TURN RIGHT'.
- This is because we assume that on primary roads ( freeways , major highways , and minor highways ), turn angles are less than 45 degrees (no sharp turns on higher-throughput roads). Therefore, you never have something called an "exit" that has such an angle, and the instruction should be TURN, not EXIT.
- If s-in is a primary road ( FW , MH , mH ) and s-out is not a primary road ( FW , MH , mH ), the instruction is: 'EXIT RIGHT'.
- If s-in is a ramp/exit and s-out is neither a primary road ( FW , MH , mH ), nor a ramp/exit , the instruction is: 'EXIT RIGHT'.
- NOTE: in a RHT country there is no EXIT LEFT, in a LHT country there is no EXIT RIGHT.
- If none of the above conditions are met, the instruction is: 'KEEP RIGHT'.
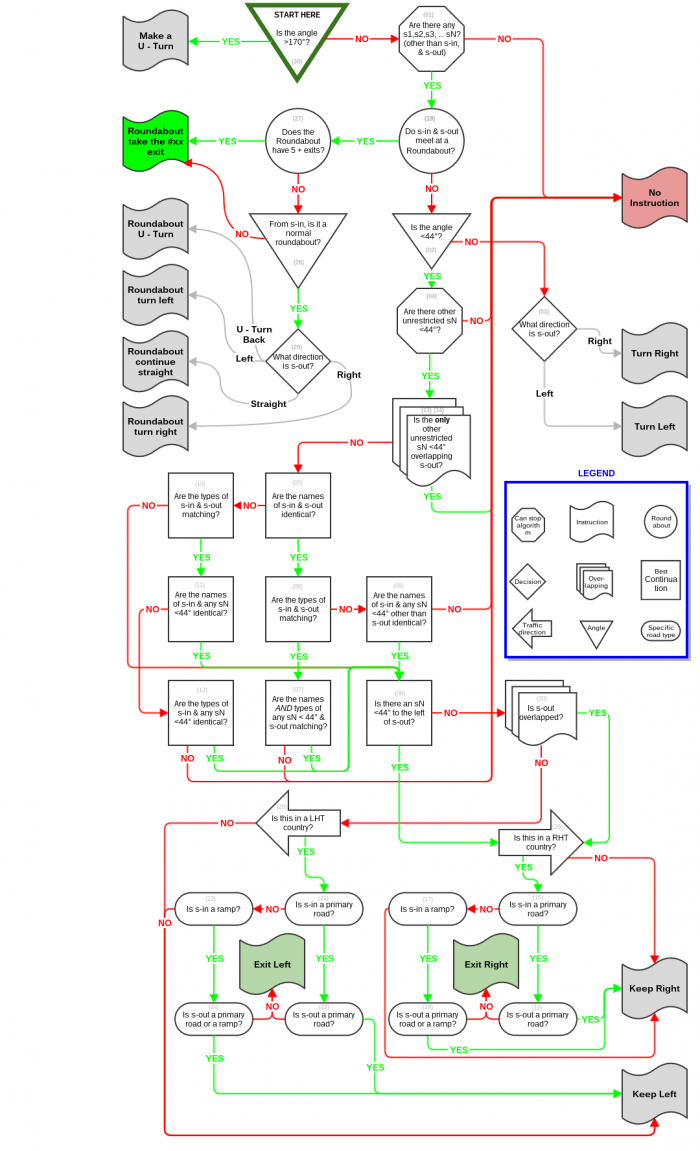
Graphic flowchart
This is a static graphic flowchart starting from a junction point and flowing through (all) the possible configuration options, to hopefully cover any scenario. It culminates in all the possible navigation instructions. This chart includes roundabouts, Left Hand Traffic, and Right Hand Traffic. For an interactive version with more descriptions and illustrations see the interactive page.
Special considerations
- The direction of a turn which is less than How Waze determines turn / keep / exit maneuvers/Stay threshold is measured relative to the other segments at the junction less than How Waze determines turn / keep / exit maneuvers/Stay threshold.
- A junction with two segments that are less than How Waze determines turn / keep / exit maneuvers/Stay threshold will give a KEEP RIGHT to the right branch, even if it is to the left of a straight line.
- When there are more than two segments less than How Waze determines turn / keep / exit maneuvers/Stay threshold, only the left most segment will be KEEP LEFT, all the rest will be KEEP RIGHT.
- If the left most segment is overlapping another segment, it will also be KEEP RIGHT.
- If the only two segments less than How Waze determines turn / keep / exit maneuvers/Stay threshold overlap each other, neither will get an instruction.
- In some cases, a junction node could have more than two segments, but the routing server will only consider two of them as valid and therefore, the maneuver will be 'Continue straight'. This happens when turns into some of the segments are restricted, the routing server then skips those segments and ingores them when determining the 'Best Continuation'.
- At the time of this writing, neither the author or anyone involved in the discussion has ever experienced this unless the restricted segment has a turn angle of less than How Waze determines turn / keep / exit maneuvers/Stay threshold.
- Turns can be restricted or unrestricted. In specific scenarios you may not be able to see this in WME - see RevCons for more information. There are external scripts which show this information (and some allow it to be easily corrected).
- The original text mentions special behavior for locked nodes. For example, in this case (image below) - assuming the node is locked - heading south, the right turn will be considered 'Continue straight' as the routing server has no other option and there's only one possible segment to be s-out.
- If the node was not locked, it is most likely that Waze would tell you to turn right. Driving against the direction is a high penalty, and so is a left turn where a turn is not allowed. However, it would still have been an option, which is why the routing server would have called it 'turn right'.
- This could be confusing, especially since there's no external indication on whether or not a node is locked at the moment.
- The author and those involved in the discussion have never experienced a locked node which didn't follow the algorithm for determining the instruction.
