| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
Now that the paths of A to F, and A to E are being measured separately, the traffic jam for the red cars turning at D does not have a negative effect on the blue cars going straight through D. Their ETAs are being recorded separately. | Now that the paths of A to F, and A to E are being measured separately, the traffic jam for the red cars turning at D does not have a negative effect on the blue cars going straight through D. Their ETAs are being recorded separately. | ||
{{Anchor|Fixing update request example}} | |||
{{Collapsible section top}} | {{Collapsible section top}} | ||
{{HighlightBar|'''Fixing update request example'''}} | {{HighlightBar|'''Fixing update request example'''}} | ||
| Line 55: | Line 56: | ||
Thus, [[Glossary#Update_Request|URs]] resulting from the inability to distinguish left turn delays from straight through traffic can be dealt with using the junction box. Draw a junction box over the intersection where the straight traffic is being improperly detoured, in order to provide better data collection and hopefully better routing. U-turns that are legal should not be restricted. | Thus, [[Glossary#Update_Request|URs]] resulting from the inability to distinguish left turn delays from straight through traffic can be dealt with using the junction box. Draw a junction box over the intersection where the straight traffic is being improperly detoured, in order to provide better data collection and hopefully better routing. U-turns that are legal should not be restricted. | ||
[[File:JBRoutingExample1.png|400px]] | [[File:JBRoutingExample1.png|400px]]</br> | ||
<small>[[#Fixing update request example|Link to fixing update request example]]</small> | |||
{{Collapsible section bottom}} | {{Collapsible section bottom}} | ||
{{Anchor|Understanding inside a junction box example}} | |||
{{Collapsible section top}} | {{Collapsible section top}} | ||
{{HighlightBar|'''Understanding inside a junction box example'''}} | {{HighlightBar|'''Understanding inside a junction box example'''}} | ||
| Line 64: | Line 67: | ||
{{mbox|text=''There are many types of scenarios where a junction box may be indicated, this sample is used just to explain the function of a junction box, and not meant as guidance on where to use them.''}} | {{mbox|text=''There are many types of scenarios where a junction box may be indicated, this sample is used just to explain the function of a junction box, and not meant as guidance on where to use them.''}} | ||
[[File:Junction Box 3a.png|right|250px]] | [[File:Junction Box 3a.png|right|250px]] | ||
To illustrate the improving data collection concept, let's take a look at this intersection. There are five segments entering/exiting the junction box (segments which are only partially inside the junction box). There is one segment which is wholly inside the junction box. If there were no junction box at this intersection the individual [[Routing server#Turn delays|turn delay]] ''AKA the time it takes to turn from one segment to the next'' data for the outer five segments would be merged together at the inner four segments, and be distorted. The junction box here alleviates the problems with collecting accurate turn delay transition timing caused by the short segments in the middle. | To illustrate the improving data collection concept, let's take a look at this intersection. There are five segments entering/exiting the junction box (segments which are only partially inside the junction box). There is one segment which is wholly inside the junction box. If there were no junction box at this intersection the individual [[Routing server#Turn delays|turn delay]] ''AKA the time it takes to turn from one segment to the next'' data for the outer five segments would be merged together at the inner four segments, and be distorted. The junction box here alleviates the problems with collecting accurate turn delay transition timing caused by the short segments in the middle.</br> | ||
<small>[[#Understanding inside a junction box example|Link to understanding inside a junction box example]]</small> | |||
{{Collapsible section bottom}} | {{Collapsible section bottom}} | ||
{{Anchor|Timing example}} | |||
{{Collapsible section top}} | {{Collapsible section top}} | ||
{{HighlightBar|'''Timing example'''}} | {{HighlightBar|'''Timing example'''}} | ||
| Line 74: | Line 80: | ||
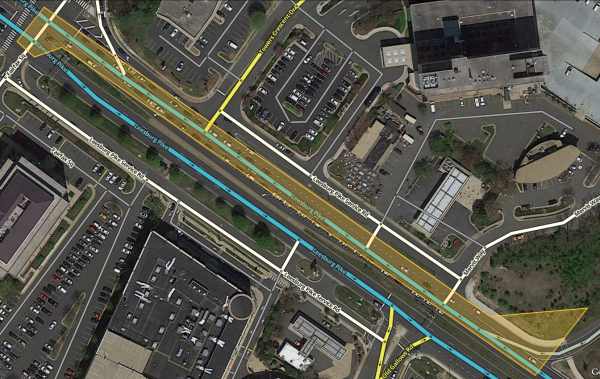
A route path from point A to point B (westbound Mill Grove Rd to southbound Idlewild Rd to westbound Indian Trail Fairview Rd) is treated as a single transition, even though in actuality it traverses four segments (3 transitions). The green path is the actual junction box route in WME. | A route path from point A to point B (westbound Mill Grove Rd to southbound Idlewild Rd to westbound Indian Trail Fairview Rd) is treated as a single transition, even though in actuality it traverses four segments (3 transitions). The green path is the actual junction box route in WME. | ||
<center>[[File:Timing_Junction_Box_4e.PNG|300px]] [[File:Junction Box B.png|300px]]</center> | <center>[[File:Timing_Junction_Box_4e.PNG|300px]] [[File:Junction Box B.png|300px]]</center></br> | ||
<small>[[#Timing example|Link to timing example]]</small> | |||
{{Collapsible section bottom}} | {{Collapsible section bottom}} | ||
{{clear}} | {{clear}} | ||
Revision as of 00:58, 7 September 2021
| Currently, junction boxes require rank 4 or higher to create or edit them. |

A junction box (JB) is a tool used to group separate junction nodes and the segments between them into a single big junction for improved data collection, routing control and navigation instructions. In simple terms, junction boxes tell the routing server, “Although the segments coming into here are connected in a few separate places, they should be treated as if they all connected together at one place." Because of this, junction boxes provide an extra layer of information on top or instead of the information associated with individual nodes, segments and turns.
Overview
The junction box enables a complex intersection, or interchange composed and displayed as multiple segments to be treated by the routing server as a single junction node with multiple inputs and outputs. Considering a complex intersection as a single point has several beneficial properties:
- Traffic speed data for each path through the junction box can be collected separately.
- Turn restrictions can be separately controlled for each path through the junction box.
- Voice prompts can be separately controlled for each path through the junction box.
- Turn instructions can be separately controlled for each path through the junction box.
- Additional beneficial features of a junction box will be listed here as they become available.
For ETA purposes, the routing server does not consider segments wholly within the junction box, but rather treats the junction box as if all the segments which enter or exit the the junction box are connected to a single junction node.
Junction boxes are considered only by the routing server. Junction boxes have no visibility in the client or on the live map. Junction boxes do not affect the search engine; the origin or destination of a route may be contained in a junction box.
Improving data collection

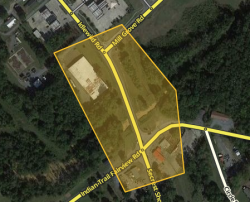
Let's look at how a complex intersection can skew turn delay transition speed data. Take the following intersection for example. It seems at first glance like a pretty simple intersection, but if it usually experiences heavy traffic this intersection could be collecting bad data.

Assume that all the roads are two-way and all turns are enabled. Consider the drivers going from A to E, and from A to F, when there is a traffic jam for the left turn (at point D), but traffic going straight through D is flowing fine.
Without the junction box, the traffic from point A to point C is considered to be the same for both the red and the blue cars. The same statistical data is gathered and the average speed skews the ETA for everyone. The turn delay data is only different for the red and blue cars on the one segment before the turn at D, from C to D.

The junction box solves this problem.
With the junction box, historical and real time data are collected separately for each one of the possible routes through the intersection - all 12 of them.
- A ➡ B
- A ➡ E
- A ➡ F
- B ➡ A
- B ➡ E
- B ➡ F
- E ➡ A
- E ➡ B
- E ➡ F
- F ➡ A
- F ➡ B
- F ➡ E
Now that the paths of A to F, and A to E are being measured separately, the traffic jam for the red cars turning at D does not have a negative effect on the blue cars going straight through D. Their ETAs are being recorded separately.
Turn arrow tooltip on a junction box exit arrow
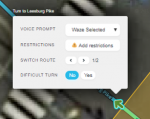
The turn arrow tooltip has five elements: Voice prompt, Instructions (visual instructions), Restrictions, Switch Route (when applicable), and Difficult turn. Junction boxes have no effect on these elements, unless these elements are changed in the turn arrow tooltip.
Voice prompt
- If a voice prompt is added in the junction box's exit arrow tooltip, then all internal Waze selected voice prompts are removed and the voice prompt is announced at the first junction node using the first named road segment on that route from the first junction node.
- If a voice prompt is added in the junction box's exit arrow tooltip, the voice prompt will be given at the first junction node. Unless there is an editor selected voice prompt (other than Waze selected) on a node along the path, then the editor selected voice prompt on the node will override the junction box' exit arrow voice prompt (junction box's exit arrow voice prompt will not be given).
- If a voice prompt is added in the junction box's exit arrow tooltip, and lane guidance has also been added to the segment entering the junction box at the first node inside the box, the lane guidance will be displayed with the voice prompt. This can be undesirable, and it is recommended to check the lane guidance when adding a voice prompt to junction box paths.
Visual instructions
Visual instructions can be added to a junction box's exit arrow.
- Just like voice prompts, visual instructions will be given at the first node that the path encounters through the box.
- Unlike JB voice prompts, JB visual instructions will work together with subsequent node-based visual instructions inside the junction box. In these cases the junction box's visual instruction will be shown at the first node, and then the node-based visual instruction(s) will be shown at the subsequent node(s) through the junction box.
- When adding visual instructions to a junction box's exit arrow do not add visual instructions directly to the first node of that route, to avoid a conflict between the junction box's visual instruction and the node-based visual instruction on that first node.
- Both node-based and junction-box-based visual instructions require an associated navigation instruction in order to be visible in the app, either resulting from default behavior, a voice prompt or a View and hear lanes override. If the driver is not told to turn, exit, continue, etc. at a node, no visual information can be displayed there.
Adding visual instructions to a junction box route is useful for situations where multiple signs are displayed for a single turn, with each sign pertaining to the next turn. For example, in complex interchanges it's common to have multiple lanes exit the highway together at one place and then split apart a short distance after exiting, with the different lanes marked by different signs. Using a JB visual instruction allows the driver to see only the visual instructions that pertain to their route.
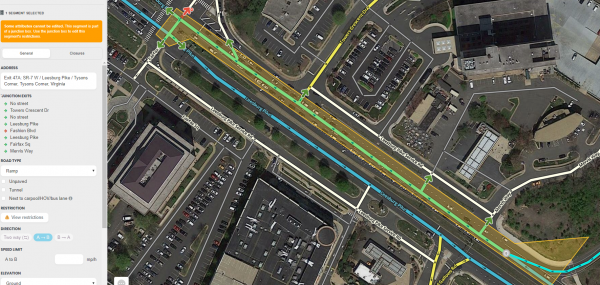
Restrictions
Partial restrictions, including time-based restrictions, can be added to junction box paths just like they are to normal node-based turns. In fact, when a junction box is created, any partial restrictions that existed on segments and turns within the box are automatically copied into the applicable junction box paths, making these JB exit arrows yellow. This is similar to how drawing a JB over nodes with full turn restrictions causes applicable JB paths to have red exit arrows. After a junction box is created, all restrictions are controlled by hovering over its exit arrows and making changes there rather than on underlying segments or turns.
Internal turn restriction(s)
The turn restrictions or time based turn restrictions for junction arrows on segments that enter the junction box are visible on the junction node within the junction box as of January 2020. Selecting that segment displays turn restrictions just like selecting a segment that is not in a junction box. There are also turn restrictions or time based turn restrictions on each exit arrow of a junction box route, this is because the junction box has taken over the exit from the entry segment and this(these) turn restriction(s) is(are) now the turn restriction(s) on the junction box exit. The same is true for time based segment restrictions on segments that enter the junction box.

Switch Route
There can only be one route from a specific entrance to a specific exit in a junction box. In cases where there is more than one routing option available, then the Switch Route option will appear. The switch route option will allow you to select the appropriate route through the junction box. The allowed route through a junction box should always be enabled and shown with the green path. A red exit turn arrow means that any route from the selected entry segment to the selected exit turn arrow will be disabled
Difficult turn
Difficult turns and time based difficult turns are available on junction box routes the same way they are used on segment turn arrows.
- Junction box difficult turns may be useful for paths that are legal but directly contradict guide signs and/or require quick weaving through multiple lanes of traffic, such as entering a highway from the right and then quickly exiting to the left.
Controlling turns
Junction boxes permit disabling multi-segment turns that are difficult to control in complex intersections. Without a junction box, controlling complex turns may require adding artificial segments and/or reducing the intersection to a single point using a bow-tie configuration.
Where to use
Junction boxes are suitable only where their functions are required. If problems are easily solved with other features such as turn restrictions, a junction box should not be used. Appropriate reasons to use a junction box:
- To prohibit a route on the same exit path when there are two different entrances, where using a regular turn restriction would also prohibit other routes that should be allowed.
- To prohibit U-turns in one or more directions on median segments between divided roads at H or # intersections
- To disable improper U-turn prevention that would otherwise be activated by the natural geometry of an intersection
- To collect more granular data on traffic that backs up unequally across different lanes of a road through multiple junction nodes, due to conditions like heavy weaving between entrances and exits on a freeway, or busy left turns through an intersection with long cycle times
- To ensure proper routing and data collection through intricate intersections containing multiple short segments
- To provide more appropriate voice prompts for movements through intersections, where segment geometry and node-based voice prompts would provide improper navigation instructions
- To provide more accurate turn instructions for a turn with multiple signs for different destinations past the turn
- To correct routing issues or improper turn instructions in roundabouts
Drawbacks
Certain things cannot be done to segments and nodes that are part of a junction box without first deleting the junction box. These include:
- Changing a segment's direction between two way and one way
- Moving a junction node across the boundary of a junction box
- Adding or deleting a junction node inside a junction box
- Adding, deleting, connecting or disconnecting a segment inside a junction box
For these reasons, junction boxes should not be used for every intersection. Where they are used, turn information should be applied to node-based turns rather than junction box paths, if possible, to avoid rework if the junction box needs to be deleted in the future.
Note that for many years it had been impossible to cut or merge a segment, even if only an end of it was part of a junction box; the junction box had to be deleted first. This is no longer true.
Overriding U-turn prevention
A junction box will override U-turn prevention if one or more of the junction nodes are inside the junction box. Unless a prohibited turn restriction prohibits both the left turn and one turn for the U-turn.
There are three cases to consider:
- U-turn prevention is properly set up and a junction box is installed over all or part of the intersection. All u-turns previously prevented by the three criteria are now allowed - unless prohibited by the junction box
- U-turns are allowed by the intersection's segment geometries but the junction box is able to prevent the u-turn by having its turn restriction prohibited
- A prohibited turn restriction prevents a left turn and a U-turn inside a junction box; the junction box is not able to override the red turn restriction and neither path will show up as an option in the junction box.
- If the JB has a <14 m segment that only has one of its nodes within the JB then the u-turn is allowed. (Even if u-turn prevention is properly set up since the JB acts like another node (median is seen as two segments) and the u-turn is routed).
After the junction box is set up, the selected pathways through it supersede the segments' turn restrictions on the pathway within it. Therefore, if a segment's turn restriction within the pathway is later changed, that change is ignored and the pathway(s) selected through the box are not affected.
Editing
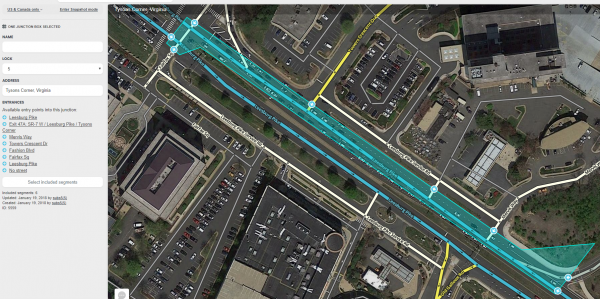
A Junction box is created by selecting Junction box from the draw segments menu (Shortcut key J). Click at one vertex of the junction box. Continue to click at each vertex of the box until the box surrounds all the junction nodes of the intersection. Double click to complete the box.
- The boundaries of the box cannot be changed once created. If you need to change the shape of the junction box, you must delete it and create it again.
- Before creating a junction box at an intersection, make sure that there are no incorrect turn restrictions including U-turns. Routes through the junction box that are prevented by existing turn restrictions cannot be enabled in the junction box.
- The routes through a junction box can be edited when it is selected. To select a junction box, click on it.
- When the junction box is selected, the left pane will show the potential connection paths through the junction box as illustrated above. Clicking the check box next to each connection path toggles between enabling or disabling routing between the indicated entry/exit pair.
- The left pane includes a button to "Select included segments." Clicking this button will select all the segments with both ends in the junction box (these are the segments that are not considered for ETA routing purposes).
- The left pane includes a name box and an address. A name can be added to the name box and the address may be edited. However, currently the name and address of a junction box has no effect.
- To delete a junction box, select the junction box and click the delete button
 (Shortcut key Del).
(Shortcut key Del). - Changes to junction boxes (and adding new junction boxes) require a tile update to affect routing.
Effects In Editor
Junction boxes can only be edited by editors of at least rank 4. Junction boxes appear in the Waze Map Editor when the Junction Boxes layer is turned on; the two pieces of paper in the upper right of the map editing area. Junction boxes appear as a polygon around all the junction nodes of an intersection.
All segments that enter the junction box are only partially editable. Selecting a segment that is part of a junction box results in a message: "Some attributes cannot be edited. This segment is part of a junction box. Use the junction box to edit this segment's restrictions." For further details on which attributes can be edited and which cannot, see when to use.

Selecting the junction box causes the left pane to display the junction box properties. The properties show the editor that created the junction box with the date and the editor of the last update to the junction box. If changes are needed to the junction box or segments associated with the junction box, contact the identified editor or other rank 4 or higher editor in your area.
The left pane shows potential entry/exit pairs with a check box ticked for each pair enabled for routing. Note that only entry/exit pair paths which are fully visible on screen are displayed. So make sure you can see the whole boundary of the JB to be sure you're getting a full list of entry/exit pair connections in the left pane.
- Routes through the junction box that pass through a single junction node (and do not cross any JB internal segments) are not controlled by the JB. Instead, they are controlled by turn restrictions in place when the junction box is created.
- Routes through the junction box that are prohibited by red turn restrictions between segments within the junction box are not considered.
- Difficult turns can be set on the junction box's turn restrictions and do affect routing in the server if the user has the appropriate setting selected.
- Any green or yellow turn restriction on a junction box can have the difficult turn attribute added for either 24/7 coverage or with time/day/date restrictions. Please refer to the Difficult turn section for editing directions.
Switch route selection

- Select the entry segment of the junction box that you want to compare routes on.
- Hover over the appropriate exit turn arrow that you want to select the desired route.
- The switch route selection will appear between the restrictions and difficult turn options in the turn arrow tooltip box.
- Click the forward or back arrow to cycle thru the allowable routes.
- For a route that you wish to allow, always select the green route from the entry segment to the exit turn arrow. In other words do not select a route that should be disabled, select the route that should be allowed.
- A red arrow on the exit turn arrow means that any route from the selected entry segment to the selected exit turn arrow will be disabled
If there is only one route available in the junction box then the switch route selection will not appear. Note it may take several clicks to get to the desired route.
Errors when editing
- Max size - The length of a junction box cannot exceed 0.01° latitude and 0.01° longitude. In terms of distance, the north-south linear limit is always 1110m (0.01°), while the maximum east-west linear limit varies depending on your latitude, because the length of a longitudinal degree decreases as you travel further from the equator. In the southernmost part of the continental US, 0.01° longitude translates to about 1010 m; along the Canadian border (49° N), however, 0.01° longitude is about 730 m. So the max size of a JB in Key West is about 1110 m x 1010 m (N-S "height" × E-W "width"), but along the Canadian border the max size of a JB is 1110 m x 730 m (N-S "height" × E-W "width").
- Two junction node minimum - A junction box must include at least two junction nodes. Two junction nodes within the junction box must be connected by a segment. A junction box with only one junction node cannot be saved.
- No overlapping - A junction node cannot be included in multiple junction boxes.
- Sixteen paths max - No more than 16 controllable entry/exit paths can pass through a single-junction node within a junction box. A save error occurs if a junction node has more than 16 connections. This also counts the adjacent connections not displayed in the routing box list that do not cross any of the internal segments like A to G, D to J, etc.
- Enabled U-turn on a two-way segment - Note that having U-turn(s) enabled on a two-way segment inside the junction box will increase the number of paths and can lead to the saving error message.
- Non-navigable segments - Junction nodes within a junction box can't be connected to non-drivable road types unless connected by a virtual node. Connected non-drivable road types will generate a save error and should be disconnected from the junction within the junction box.
Adding complexity
Adding segments or junction nodes to an intersection to workaround the "one connection for every entry/exit pair" and "no more than 16 connections per node" limitations is not recommended. If such a workaround is required, please consult with your country manager or regional coordinator.
Final Checks
- For the final configuration, if there is not an allowed path from the entrance segment to the exit segment then there needs to be a red turn restriction arrow and red route/path.
- For the final configuration, if there is an allowed path then there needs to be a green (or yellow) turn restriction arrow and a green route/path.
- It is recommended to save the final configuration of the junction box, then either soft or hard refresh the map. After these steps recheck every route from every possible entry segment to each exit segment. This is recommended because occasionally during the save process WME will set an incorrect route and rechecking each route through through the junction box will catch these errors.